English Plural Nouns Pdf
English Plural Nouns Pdf' title='English Plural Nouns Pdf' />Plural Wikipedia. The plural sometimes abbreviated. PL, in many languages, is one of the values of the grammatical category of number. Plural of nouns typically denote a quantity other than the default quantity represented by a noun, which is generally one the form that represents this default quantity is said to be of singular number. Most commonly, therefore, plurals are used to denote two or more of something, although they may also denote more than fractional, zero or negative amounts. English Plural Nouns Pdf' title='English Plural Nouns Pdf' />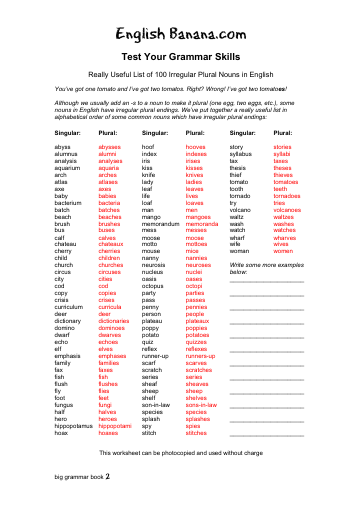 A few English nouns do not change when inflected into the plural. These are known as invariant nouns or invariable nouns. A related class are certain. This version of I Have, Who Has is a great way to review regular and irregular plural nouns. My students love playing this game, and I hope yours do too This version. An example of a plural is the English word cats, which corresponds to the singular cat. Words of other types, such as verbs, adjectives and pronouns, also frequently have distinct plural forms, which are used in agreement with the number of their associated nouns. Free Software For Unblock Sites. Some languages also have a dual denoting exactly two of something or other systems of number categories. However, in English and many other languages, singular and plural are the only grammatical numbers, except for possible remnants of the dual in pronouns such as both and either. Use in systems of grammatical numbereditIn many languages, there is also a dual number used for indicating two objects. Some other grammatical numbers present in various languages include trial for three objects and paucal for an imprecise but small number of objects. In languages with dual, trial, or paucal numbers, plural refers to numbers higher than those. However, numbers besides singular, plural, and to a lesser extent dual are extremely rare. Languages with numerical classifiers such as Chinese and Japanese lack any significant grammatical number at all, though they are likely to have plural personal pronouns. Some languages like Mele Fila distinguish between a plural and a greater plural. A greater plural refers to an abnormally large number for the object of discussion. Identifying-Singular-or-Plural-Nouns-2.png' alt='English Plural Nouns Pdf' title='English Plural Nouns Pdf' />It should also be noted that the distinction between the paucal, the plural, and the greater plural is often relative to the type of object under discussion. For example, in discussing oranges, the paucal number might imply fewer than ten, whereas for the population of a country, it might be used for a few hundred thousand. The Austronesian languages of Sursurunga and Lihir have extremely complex grammatical number systems, with singular, dual, paucal, greater paucal, and plural. Traces of the dual and paucal can be found in some Slavic and Baltic languages apart from those that preserve the dual number, such as Slovene. For example, Polish and Russian use different forms of nouns with the numerals 2, 3, or 4 and higher numbers ending with these than with the numerals 5, 6, etc. Russian and nominative plural in Polish in the former case, genitive plural in the latter case. Also some nouns may follow different declension patterns when denoting objects which are typically referred to in pairs. For example, in Polish, the noun oko, among other meanings, may refer to a human or animal eye or to a drop of oil on water. The plural of oko in the first meaning is oczy even, if actually referring to more than two eyes, while in the second oka even, if actually referring to exactly two drops. Certain nouns in some languages have the unmarked form referring to multiple items, with an inflected form referring to a single item. These cases are described with the terms collective number and singulative number. Some languages may possess a massive plural and a numerative plural, the first implying a large mass and the second implying division. For example, the waters of the Atlantic Ocean versus, the waters of each of the Great Lakes. Formation of pluralseditA given language may make plural forms of nouns by various types of inflection, including the addition of affixes, like the English es ending, or ablaut, as in the derivation of the plural geese from goose, or a combination of the two. It may be that some nouns are not marked for plural, like sheep and series in English. In languages which also have a case system, such as Latin and Russian, nouns can have not just one plural form but several, corresponding to the various cases. The inflection might affect multiple words, not just the noun and the noun itself need not become plural as such, other parts of the expression indicate the plurality. In English, the most common formation of plural nouns is by adding an s suffix to the singular noun. For details and different cases, see English plural. Just like in English, noun plurals in French, Spanish and Portuguese are also typically formed by adding an s suffix to the lemma form, sometimes combining it with an additional vowel in French, however, this plural suffix is often not pronounced. This construction is also found in German and Dutch, but only in some nouns. Most languages, however, do not form plurals this way. In Welsh, the reference form, or default quantity, of some nouns is plural, and the singular form is formed from that, eg llygod, mice llygoden, mouse erfin, turnips erfinen, turnip. Plural forms of other parts of speecheditIn many languages, words other than nouns may take plural forms, these being used by way of grammatical agreement with plural nouns or noun phrases. Such a word may in fact have a number of plural forms, to allow for simultaneous agreement within other categories such as case, person and gender, as well as marking of categories belonging to the word itself such as tense of verbs, degree of comparison of adjectives, etc. Verbs often agree with their subject in number as well as in person and sometimes gender. Examples of plural forms are the Frenchmangeons, mangez, mangent respectively the first, second and third person plural of the present tense of the verb manger. In English a distinction is made in the third person between forms such as eats singular and eat plural. Adjectives may agree with the noun they modify examples of plural forms are the French petits and petites the masculine plural and feminine plural respectively of petit. The same applies to some determiners examples are the French plural definite article les, and the English demonstrativesthese and those. Microsoft Powerpoint 2010 Full Crack Indir Ve. It is common for pronouns, particularly personal pronouns, to have distinct plural forms. Examples in English are we us, etc. English personal pronouns, and again these and those when used as demonstrative pronouns. In Welsh, a number of common prepositions also inflect to agree with the number, person, and sometimes gender of the noun or pronoun they govern. Nouns lacking plural or singular formeditCertain nouns do not form plurals. A large class of such nouns in many languages is that of uncountable nouns, representing mass or abstract concepts such as air, information, physics. However, many nouns of this type also have countable meanings or other contexts in which a plural can be used for example water can take a plural when it means water from a particular source different waters make for different beers and in expressions like by the waters of Babylon. There are also nouns found exclusively or almost exclusively in the plural, such as the English scissors. These are referred to with the term plurale tantum. Occasionally, a plural form can pull double duty as the singular form or vice versa, as has happened with the word data.
A few English nouns do not change when inflected into the plural. These are known as invariant nouns or invariable nouns. A related class are certain. This version of I Have, Who Has is a great way to review regular and irregular plural nouns. My students love playing this game, and I hope yours do too This version. An example of a plural is the English word cats, which corresponds to the singular cat. Words of other types, such as verbs, adjectives and pronouns, also frequently have distinct plural forms, which are used in agreement with the number of their associated nouns. Free Software For Unblock Sites. Some languages also have a dual denoting exactly two of something or other systems of number categories. However, in English and many other languages, singular and plural are the only grammatical numbers, except for possible remnants of the dual in pronouns such as both and either. Use in systems of grammatical numbereditIn many languages, there is also a dual number used for indicating two objects. Some other grammatical numbers present in various languages include trial for three objects and paucal for an imprecise but small number of objects. In languages with dual, trial, or paucal numbers, plural refers to numbers higher than those. However, numbers besides singular, plural, and to a lesser extent dual are extremely rare. Languages with numerical classifiers such as Chinese and Japanese lack any significant grammatical number at all, though they are likely to have plural personal pronouns. Some languages like Mele Fila distinguish between a plural and a greater plural. A greater plural refers to an abnormally large number for the object of discussion. Identifying-Singular-or-Plural-Nouns-2.png' alt='English Plural Nouns Pdf' title='English Plural Nouns Pdf' />It should also be noted that the distinction between the paucal, the plural, and the greater plural is often relative to the type of object under discussion. For example, in discussing oranges, the paucal number might imply fewer than ten, whereas for the population of a country, it might be used for a few hundred thousand. The Austronesian languages of Sursurunga and Lihir have extremely complex grammatical number systems, with singular, dual, paucal, greater paucal, and plural. Traces of the dual and paucal can be found in some Slavic and Baltic languages apart from those that preserve the dual number, such as Slovene. For example, Polish and Russian use different forms of nouns with the numerals 2, 3, or 4 and higher numbers ending with these than with the numerals 5, 6, etc. Russian and nominative plural in Polish in the former case, genitive plural in the latter case. Also some nouns may follow different declension patterns when denoting objects which are typically referred to in pairs. For example, in Polish, the noun oko, among other meanings, may refer to a human or animal eye or to a drop of oil on water. The plural of oko in the first meaning is oczy even, if actually referring to more than two eyes, while in the second oka even, if actually referring to exactly two drops. Certain nouns in some languages have the unmarked form referring to multiple items, with an inflected form referring to a single item. These cases are described with the terms collective number and singulative number. Some languages may possess a massive plural and a numerative plural, the first implying a large mass and the second implying division. For example, the waters of the Atlantic Ocean versus, the waters of each of the Great Lakes. Formation of pluralseditA given language may make plural forms of nouns by various types of inflection, including the addition of affixes, like the English es ending, or ablaut, as in the derivation of the plural geese from goose, or a combination of the two. It may be that some nouns are not marked for plural, like sheep and series in English. In languages which also have a case system, such as Latin and Russian, nouns can have not just one plural form but several, corresponding to the various cases. The inflection might affect multiple words, not just the noun and the noun itself need not become plural as such, other parts of the expression indicate the plurality. In English, the most common formation of plural nouns is by adding an s suffix to the singular noun. For details and different cases, see English plural. Just like in English, noun plurals in French, Spanish and Portuguese are also typically formed by adding an s suffix to the lemma form, sometimes combining it with an additional vowel in French, however, this plural suffix is often not pronounced. This construction is also found in German and Dutch, but only in some nouns. Most languages, however, do not form plurals this way. In Welsh, the reference form, or default quantity, of some nouns is plural, and the singular form is formed from that, eg llygod, mice llygoden, mouse erfin, turnips erfinen, turnip. Plural forms of other parts of speecheditIn many languages, words other than nouns may take plural forms, these being used by way of grammatical agreement with plural nouns or noun phrases. Such a word may in fact have a number of plural forms, to allow for simultaneous agreement within other categories such as case, person and gender, as well as marking of categories belonging to the word itself such as tense of verbs, degree of comparison of adjectives, etc. Verbs often agree with their subject in number as well as in person and sometimes gender. Examples of plural forms are the Frenchmangeons, mangez, mangent respectively the first, second and third person plural of the present tense of the verb manger. In English a distinction is made in the third person between forms such as eats singular and eat plural. Adjectives may agree with the noun they modify examples of plural forms are the French petits and petites the masculine plural and feminine plural respectively of petit. The same applies to some determiners examples are the French plural definite article les, and the English demonstrativesthese and those. Microsoft Powerpoint 2010 Full Crack Indir Ve. It is common for pronouns, particularly personal pronouns, to have distinct plural forms. Examples in English are we us, etc. English personal pronouns, and again these and those when used as demonstrative pronouns. In Welsh, a number of common prepositions also inflect to agree with the number, person, and sometimes gender of the noun or pronoun they govern. Nouns lacking plural or singular formeditCertain nouns do not form plurals. A large class of such nouns in many languages is that of uncountable nouns, representing mass or abstract concepts such as air, information, physics. However, many nouns of this type also have countable meanings or other contexts in which a plural can be used for example water can take a plural when it means water from a particular source different waters make for different beers and in expressions like by the waters of Babylon. There are also nouns found exclusively or almost exclusively in the plural, such as the English scissors. These are referred to with the term plurale tantum. Occasionally, a plural form can pull double duty as the singular form or vice versa, as has happened with the word data.